In life, there are two things you can’t escape from: Death and Taxes. And as the deadline, April 15, comes close again, are you ready to pay what is due? Heck, do you even know how to pay your taxes? If you don’t, here is how to file your Income Tax Return (ITR) as a freelancer or remote worker.
Disclaimer: This article is aimed to inform the readers to have a basic understanding of taxes. Some of the rules below might be partially or wholly obsolete when specific rulings are enacted. It’s in no way intended to be a substitute for professional advice.
If you want to check how to use the eBIR Forms to file your taxes, the step-by-step guide is at the last part of the article.

Why Should You Pay Your Taxes?
A lot of Filipinos are quite hesitant in paying their taxes. I mean, why do you need to lower your take-home pay for the government? But as a responsible citizen, it’s your duty to help in nation-building.
And you can also use your ITR for specific purposes like housing loans or visa applications. You can get an accountant to fix it for you. You can even use services like Taxumo. But for those who want to fix it themselves, here’s a guide you can use.

What Taxes Do You Have to Pay
After you register as a freelancer, you need to pay percentage taxes and your income tax returns. Percentage taxes and income taxes are paid quarterly. So for the schedule of deadlines:
Quarterly Percentage Tax

Quarterly percentage taxes are levied on your gross receipts for 3%. For example, you declared 60,000 as your quarterly income. You will need to pay P1,800 (P60,000 x 3%) for that quarter.
Quarterly Income Tax

Our income taxes are collected on a quarterly basis for the first three quarters. Depending on your payment scheme (which we will discuss below), you might need to pay partially during those quarters.

Annual Income Tax
The annual income tax is levied on all your earnings for the year. Of course, partial payments during the quarter will be deducted from your total payments. The deadline for this is on April 15 of the following year.

How Do You Compute your Tax Due?
Computing the income tax due is quite complicated. But this article aims to make it simple for you. For freelancers and remote workers, you can opt for the graduated income tax or 8% income taxes in lieu of graduated rates. What is the difference?

Graduated Income Tax
You must understand that freelancers and remote workers are taxed with their net income. That means income (all your earnings) minus expenses (all related normal and necessary expenses). Afterwards, you will be taxed using these graduated tax rates.
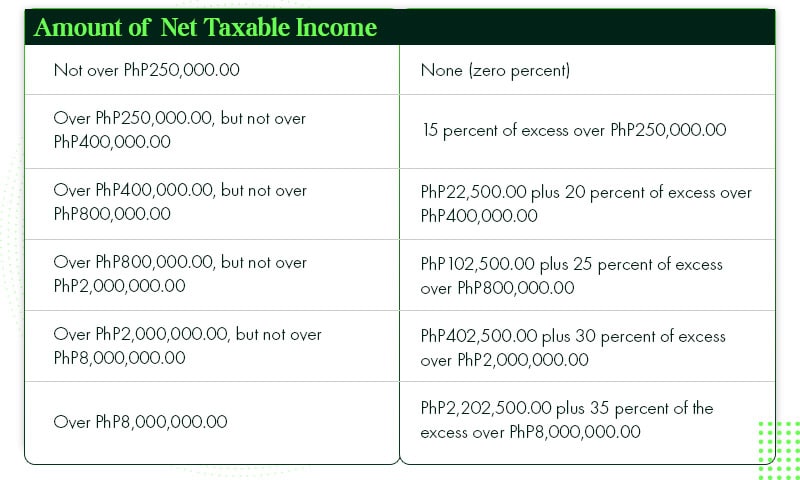 For example, you earned 300,000 PHP for the year, and you have total expenses of 40,000 PHP (like internet bills, electricity, rent, supplies, etc.). Your net income is equal to 260,000 PHP (300,000 PHP minus 40,000 PHP).
For example, you earned 300,000 PHP for the year, and you have total expenses of 40,000 PHP (like internet bills, electricity, rent, supplies, etc.). Your net income is equal to 260,000 PHP (300,000 PHP minus 40,000 PHP).
But take note, these expenses should have supporting documents. And if you have them, you can opt for Itemized Deduction.

Itemized Deduction
Itemized Deduction just means you can categorize or “itemize” the expenses. For example, you have supporting receipts for your rent, electricity bill, and such.
The advantage of this is that you can maximize all your expenses per category. The disadvantage is, you might not have all the supporting documents in place.
And if your practice doesn’t have a lot of expenses, you might not have a lot to deduct.
Optional Standard Deduction
The next option is the optional standard deduction. For this, you can have a 40% deduction of the gross earnings as a representative of your expenses. No questions asked.
So, for example, you have a total gross income of 300,000 PHP. You can deduct 120,000 PHP (40% of 300,000 PHP) from the gross income. And your net income for tax purposes is equal to 180,000 PHP.
The advantage of this is you don’t need to look for supporting documents for expenses. It’s an automatic deduction. Again, no questions asked. The disadvantage is, if your expenses are more than 40% of the gross income, you will be taxed more than you should’ve had.

8% Flat Rate in Lieu of Graduated Income Tax
The above rules can be quite complicated for most people. That’s why during the launch of the TRAIN law, another option can be used for freelancers, remote workers, and professionals.
It’s simple! For gross income above 250,000 PHP, you just need to multiply 8% from that. And you don’t have to pay for percentage tax anymore.
For example, your gross income is 500,000 PHP. You just need to pay 20,000 PHP Income tax (500,000 PHP minus 250000 PHP multiplied by 8%). It’s cheaper also because you would’ve paid 55,000 PHP if you opt for the graduated rates.
You also don’t need supporting documents for the expenses since it’s an outright percentage. The 8% option is quite convenient for most remote workers.

So Which is Better?
As a remote worker or freelancer, you have the option to choose. And it would depend on your income and expenses.
If your expected income in a year is 250k or 20,833.33 per month, it wouldn’t matter because your first 250k is non-taxable. Now, if it’s above 250k, you need to check your expenses. Let’s do a comparison.
For these scenarios, we included the 3% percentage tax to be paid by freelancers and remote workers to fully see the tax impact per scenario. What if you have a higher than 250k income? Let’s check this Scenario.
Let’s say you earn 360k PHP per year or 30k a month. And your business expenses are:
- 2000 Internet Fees
- 3000 Electricity
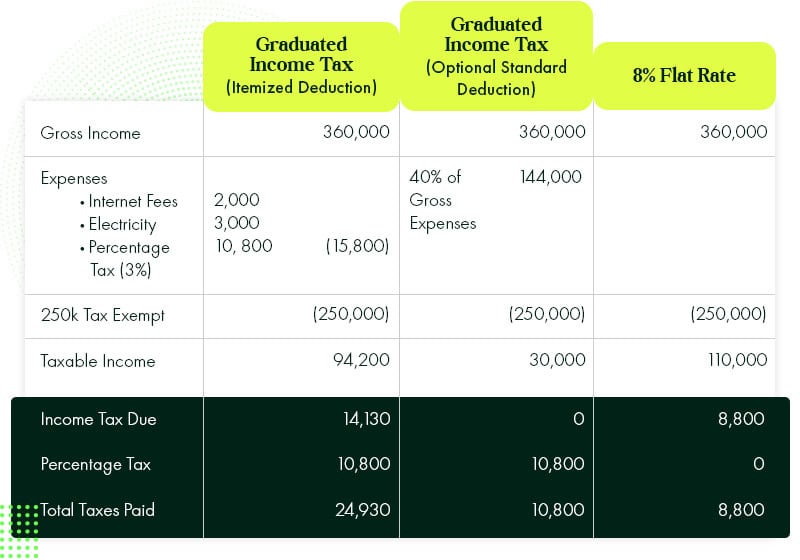
It would be best to choose the 8% flat rate because your tax due is lower compared to the graduated income tax. This is because your remote working or freelancing career doesn’t have too many attributable expenses unlike other businesses (For example, Grocery store versus freelancing).
And even if you use the optional standard deduction that yielded a 0 income tax, you still need to pay 10,800 percentage taxes. In essence, you are still saving by using the 8% because you don’t have to pay percentage taxes anymore.
Scenario B, what if your expenses are minimal compared to your income.
Let’s say you earn 600k PHP per year or 50k a month. And your business expenses are:
- 2000 Internet Fees
- 5000 Electricity
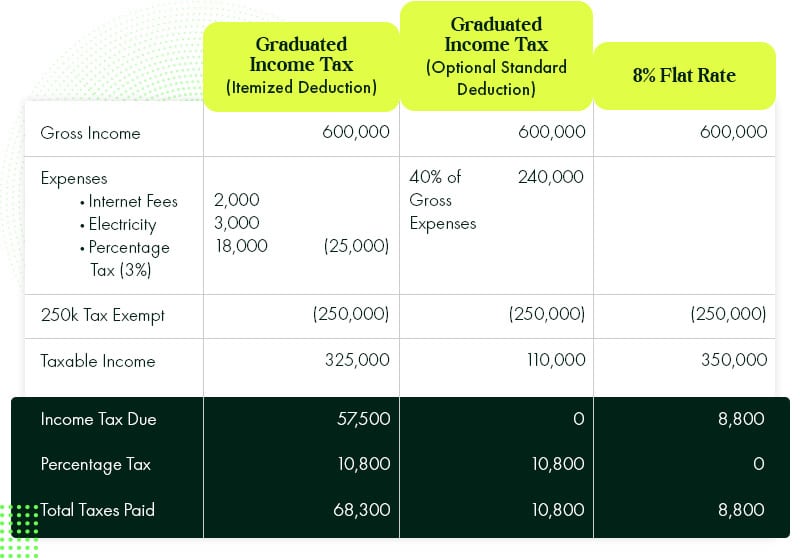
In this scenario, the 8% flat rate is still better than the graduated income options. Because the government wants to encourage freelancers and remote workers to pay their taxes. And with the uncertainty of projects they handle, the lower income tax rates compensate for that.

Filing Your Taxes
If you skipped the explanation in the first portion, here’s a tip. Know that for most remote workers and freelancers, the 8% flat rate will be the best option because of convenience. But some still opt for the graduated income taxes.
there will be three or four forms that you need to know in a year, depending on your preferred taxation type. If you opt for graduated income tax, you just need:
- Payment Form (for yearly registration renewal)
- Quarterly Percentage Tax
- Quarterly Income Tax Return
- Annual Income Tax Return
While for 8% Flat Rate in Lieu of Percentage tax, you need forms:
- Payment Form (for yearly registration renewal)
- Quarterly Income Tax Return
- Annual Income Tax Return

After choosing between the graduated income tax or 8% flat rate, you can input the figures in the eBIR Forms to electronically pass your ITR. Here’s the step-by-step guide on filing your taxes using the eBIR.
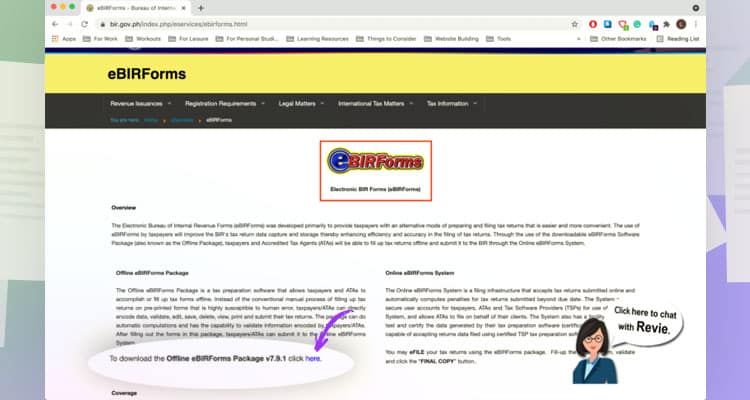
First, download your eBIR form by clicking the icon on their website. Make sure to get the latest program before filing your taxes. Remember though; this program only works on Windows operating systems.
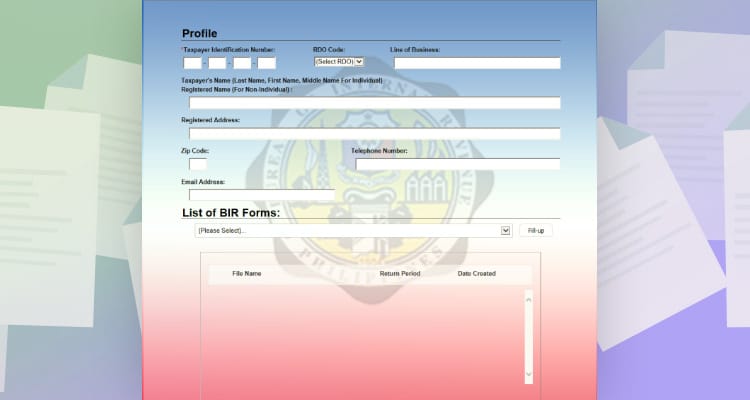
After installing the program. You will see this interface. Fill in the information and choose the form you will be filing.
BIR Yearly Registration
Every year, you need to pay the BIR for a registration fee. And you can do it online!
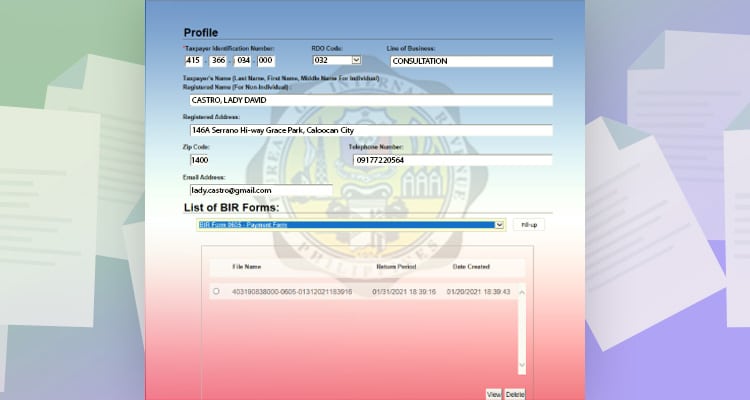
Choose BIR Form 0605 – Payment Form on the dropdown menu.
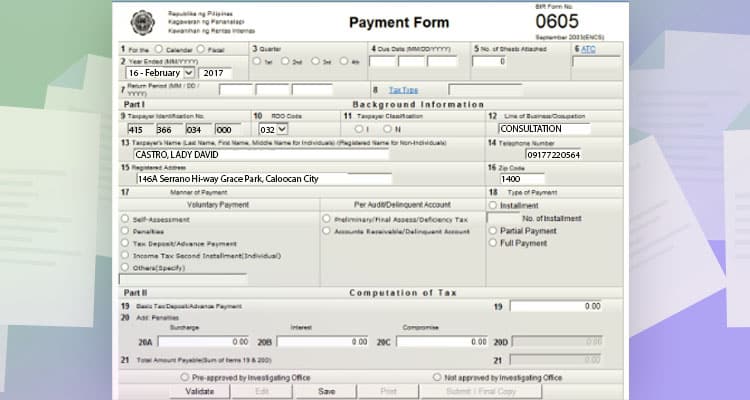
This will be the information you will input.
- Line item 1: Pick Calendar.
- Line item 2: Input the end date of the year. For example, if you’re paying for 2022, you will input “Dec 31, 2022.”
- Line item 3: Tick 1st Quarter.
- Line item 4: Input the Due date, “01/31/2022”
- Line item 10: Your RDO branch code.
- Line item 11: Tick option “I”
- Line item 12, 13, 14, 15, 16: Usually, this will be copied automatically from the information you inputted at the start of the program.
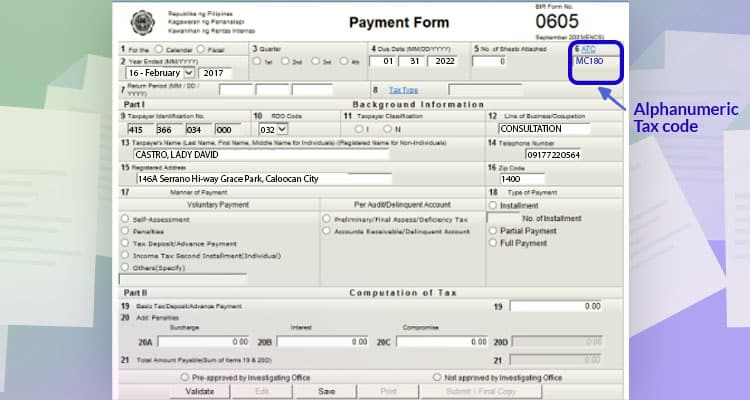
After that, click line item 6 to choose the ATC or the Alphanumeric Tax Code for the tax you will pay.
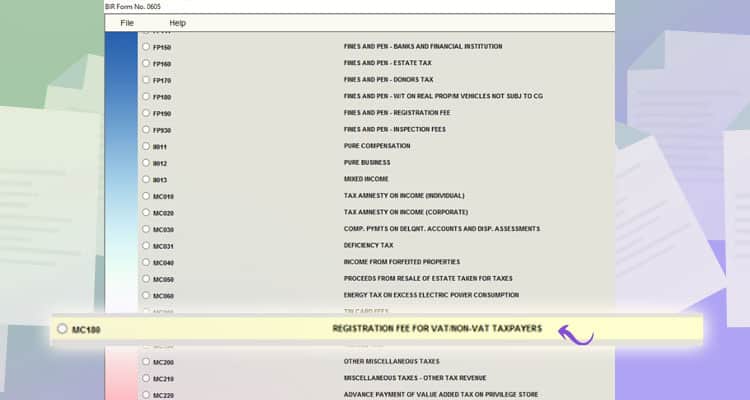
From all the choices, MC180: Registration fee for VAT/Non-VAT Taxpayers.
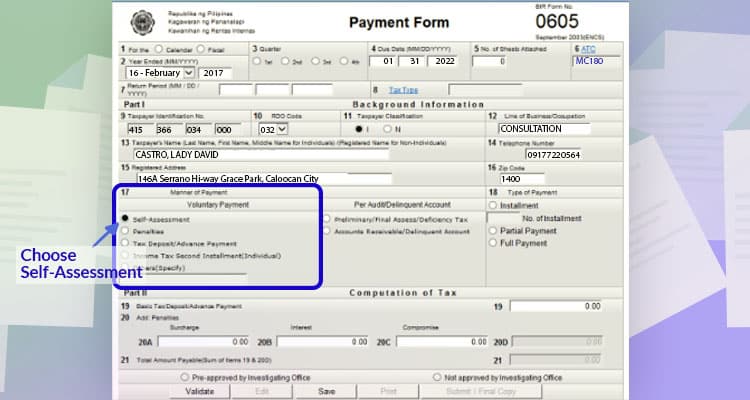
For line item 17, choose self-assessment. And then, choose full payment for line item 18.
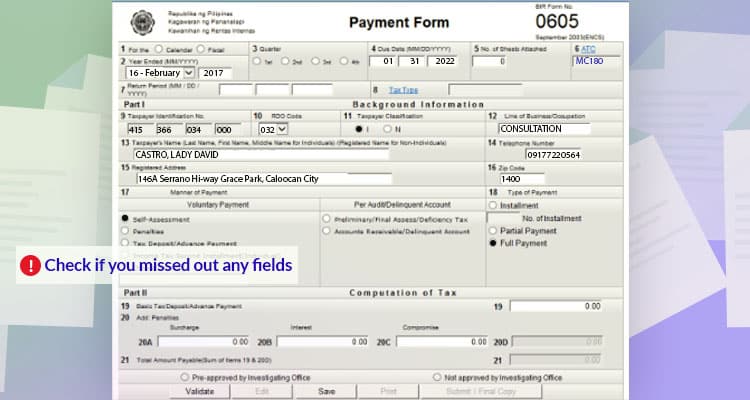
Lastly, click validate to check if there is information that you missed out on. And then, click submit/final copy.
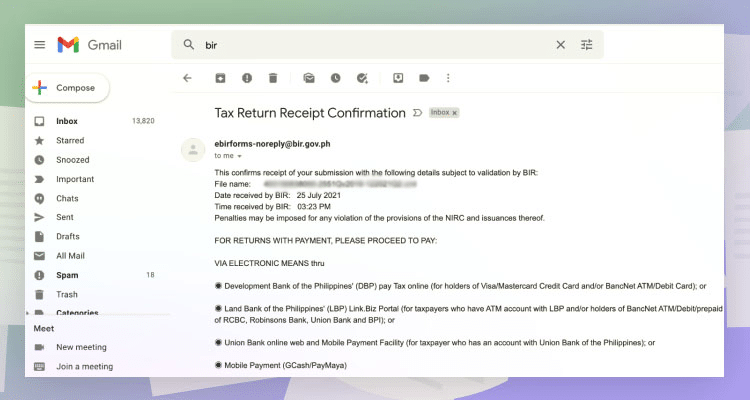
You will receive an email confirmation of your tax filing. This is your proof of filing when passing your forms to BIR and other agencies, just in case you need to.
Filing Quarterly Percentage Tax (READ EVEN IF YOU CHOSE THE 8%)
You only need to pay percentage taxes when you opt for the graduated income tax. But you have to submit this form once if you’re choosing the 8% as well. It will indicate that you are choosing the 8% tax for the calendar year.
And here’s how to do it.
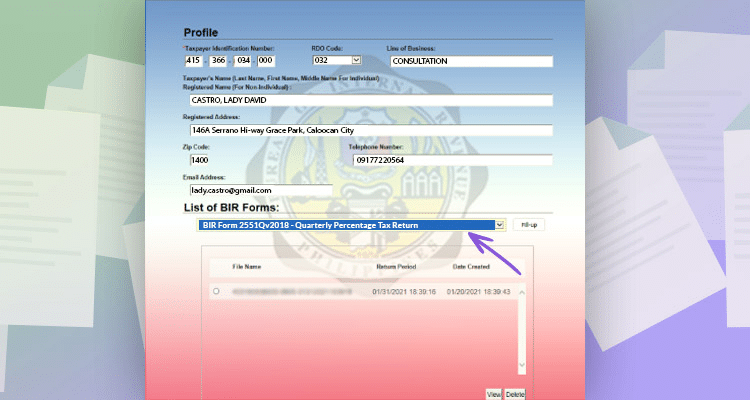
Choose BIR Form 2551Qv2018 – Quarterly Percentage Tax Return.
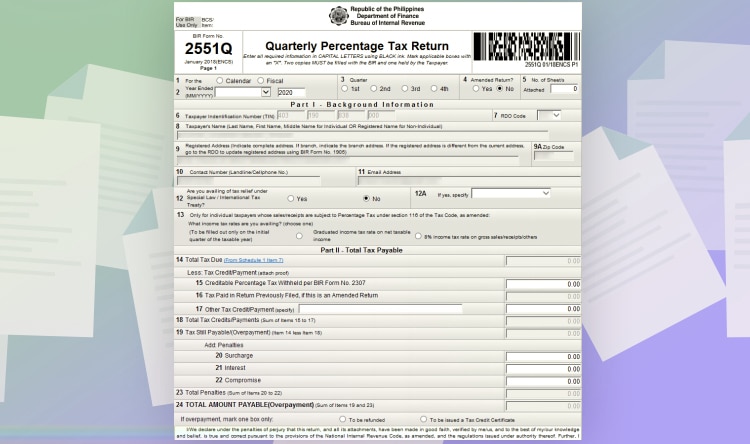
And then fill up the line items.
- Line item 1: Pick Calendar.
- Line item 2: Input the end date of the year. For example, if you’re paying for 2022, you will input “Dec 31, 2022.”
- Line item 3: Tick the quarter you want to pay.
- Line item 6, 7, 8, 9, 9A, 10, 11: For these line items, they will be copied automatically from the information you inputted at the start of the program.
- Line item 12: Choose No.
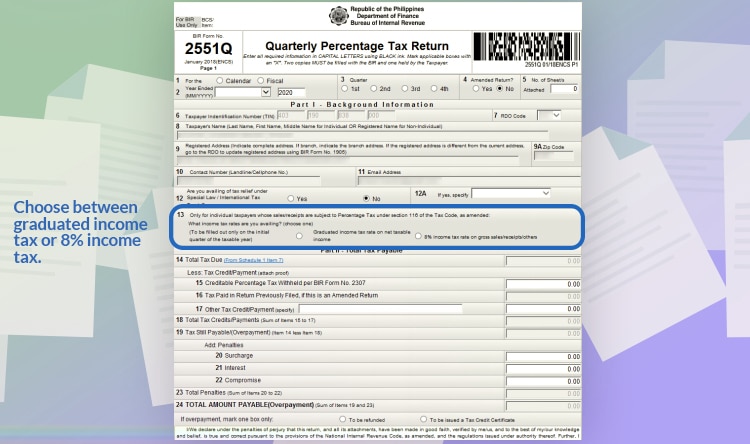
Line item 13: you have two options. Choose between graduated income tax or 8% income tax. What you will choose in the first quarter will be how you’re paying for the whole year.
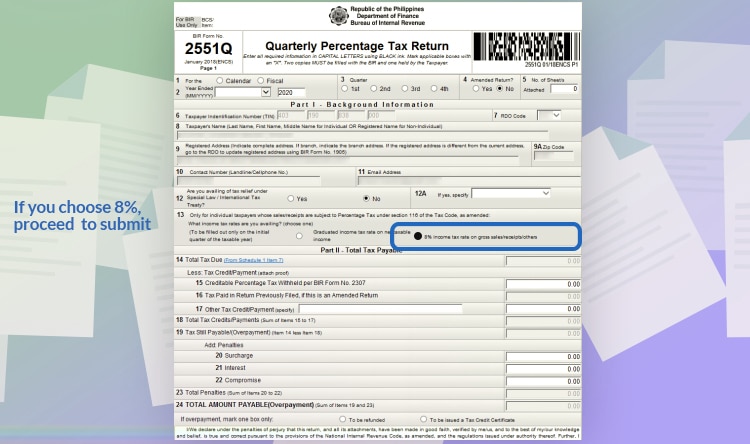
If you chose 8%, you can proceed to submit afterwards. You can skip to the last steps. Note that you only do this once if you’re choosing the 8% tax scheme. It’s just to inform the BIR that you’ll be opting for it.
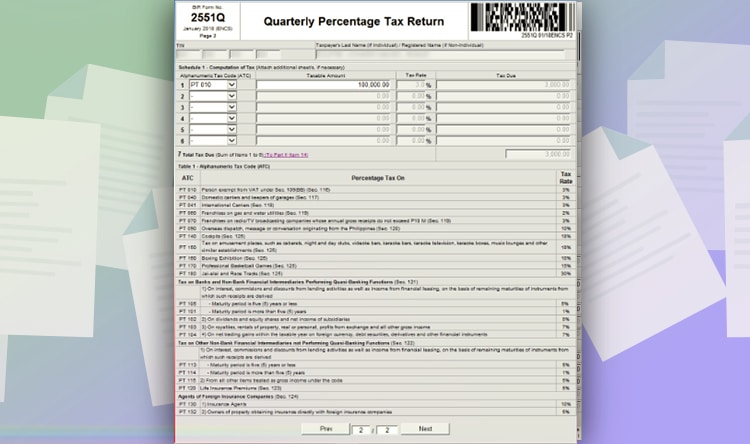
But if you chose the graduated income tax, click “From schedule 1 item 7,” on line item 14. And you will arrive at the second page. Choose PT 010 for persons exempt from VAT. And input your total gross income.
For example, your gross income or service fee before deducting all your expenses is 100,000 PHP. Just input it at the taxable amount field. The amount you will pay will be automatically computed and exported on the first page.
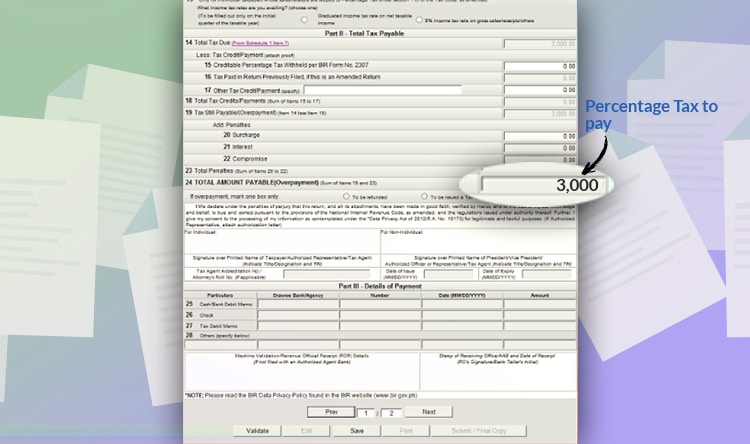
In this case, you will pay 3,000 PHP for percentage taxes. Check the details and click validate. If there is no missing information needed, you can file the form by clicking “Submit/Final Copy.”

Again, you will receive an email confirmation of your tax filing as proof of your filing.
Quarterly Income Tax
Aside from the Annual Income tax, you should also file taxes quarterly as mandated by the BIR. You do this through the quarterly income taxes. Here’s a step-by-step guide.
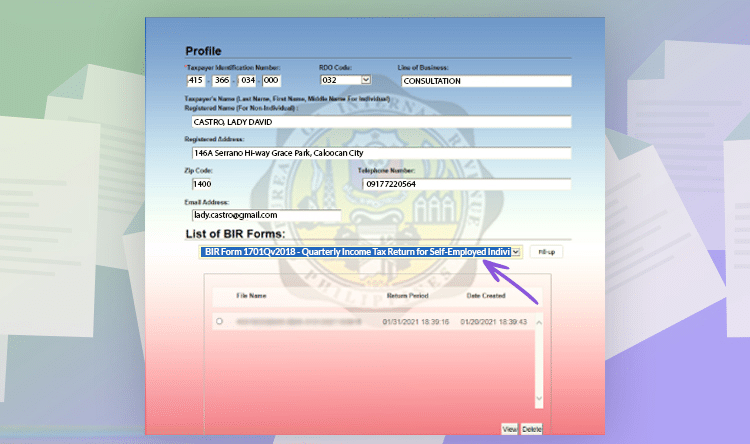
Choose BIR Form 1701Qv2018.
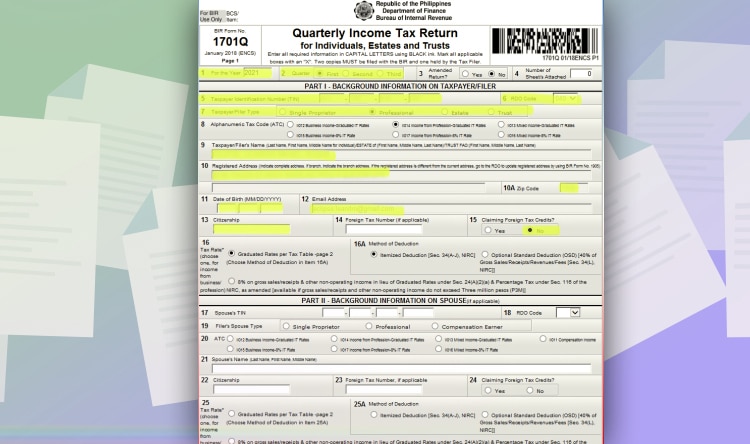
Afterwards, input the following information:
- Line item 1: Input the year you will pass the form.
- Line Item 2: Choose the quarter.
- Line Item 6: Choose your RDO Branch Code.
- Line Item 7: Tick “Professional.”
- Line Item 5, 9, 10, 10A, 12 will be automatically filled up with the information on the main menu.
- Line Item 11: Your date of birth.
- Line Item 13: Your Citizenship
- Line Item 15: Click No.
Selecting Which Tax Scheme
With the explanation in the first section of this article, there are three tax schemes you can choose from.
Make sure that you choose the tax that will be of advantage to you. What you chose from the start can’t be changed for the succeeding quarters. And here are the next sections.
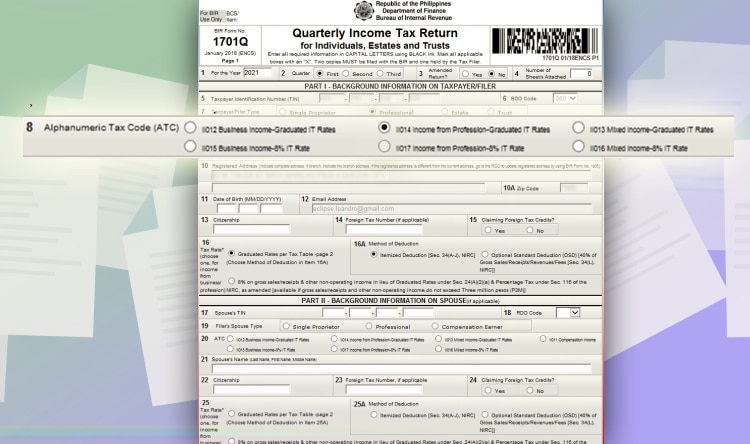
Line Item 8: Tick either “Income from Profession – Graduated IT Rate.”
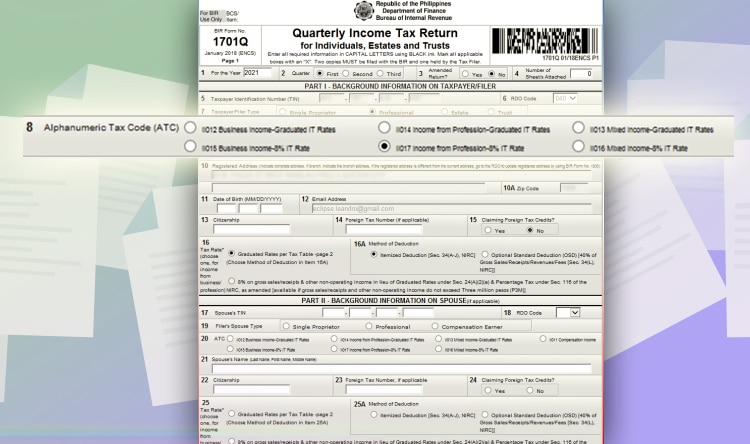
Line Item 8: Or you can also tick “Income from Profession – 8% IT Rate,” depending on your preference.
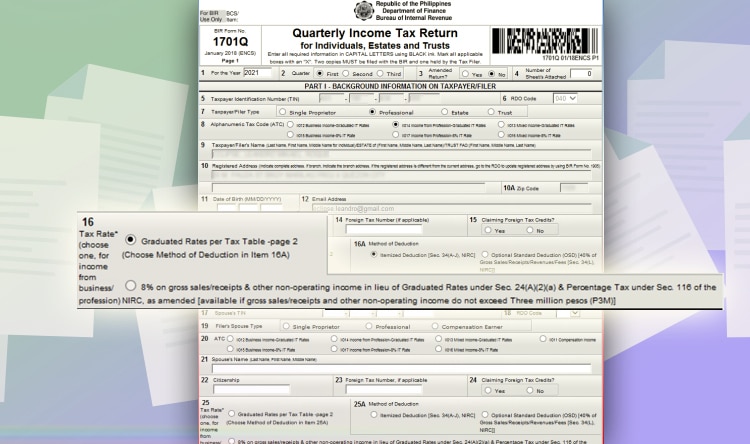
If you chose the graduated tax, choose either “Itemized Deduction” or “Optional Standard Deduction on line item 16A.” If you have chosen the 8%, continue to the next step.
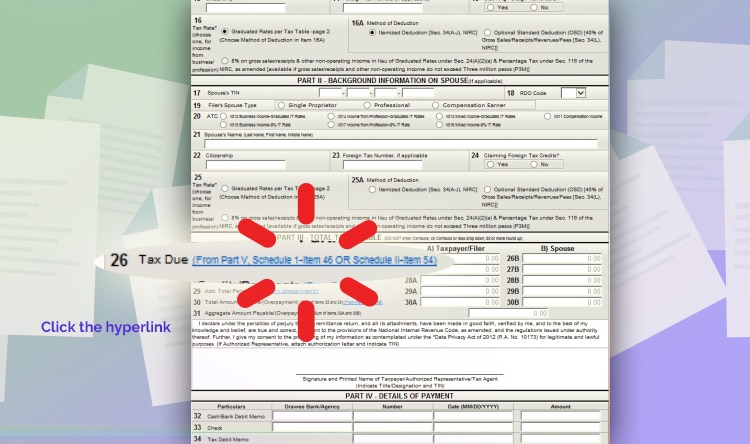
Line Item 26: Click the hyperlink beside Tax Due. You will be directed to the second page.
Quarterly Income Tax – Itemized Deductions
For the second page, you will input your expenses and income. It will differ depending on the option you chose. Here are the steps for Quarterly Income Tax – Itemized Deductions.
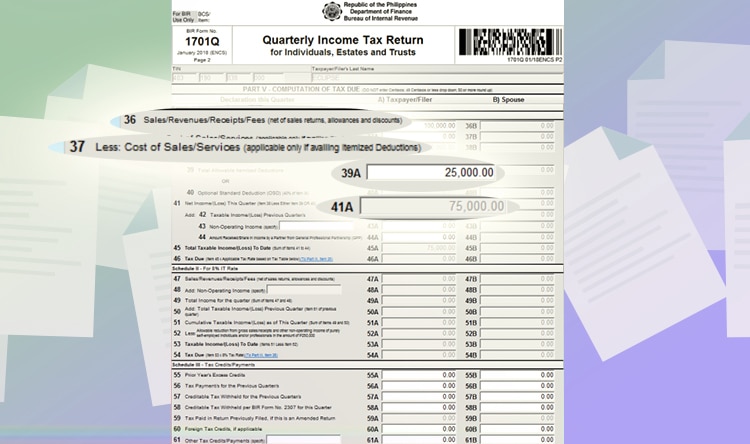
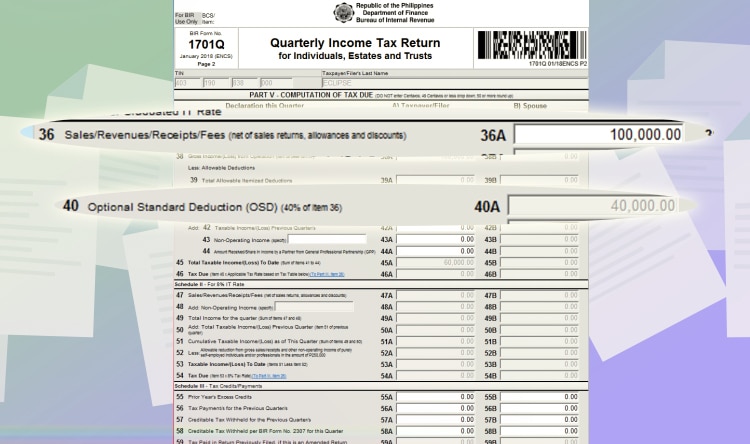
For quarterly percentage Tax – graduated income tax itemized deduction, you only need to fill up Schedule 1. Let’s say your income is 100,000 PHP and your expenses are 25,000 PHP for the quarter. Here is the information you need to supply
- Line item 36: input your sales, 100,000 PHP.
- Line item 37: input your cost if sales, if any.
- Line item 39A: Input your expenses. In this example, let’s input 25,000 PHP.
- Line Item 41 will be automatically computed.
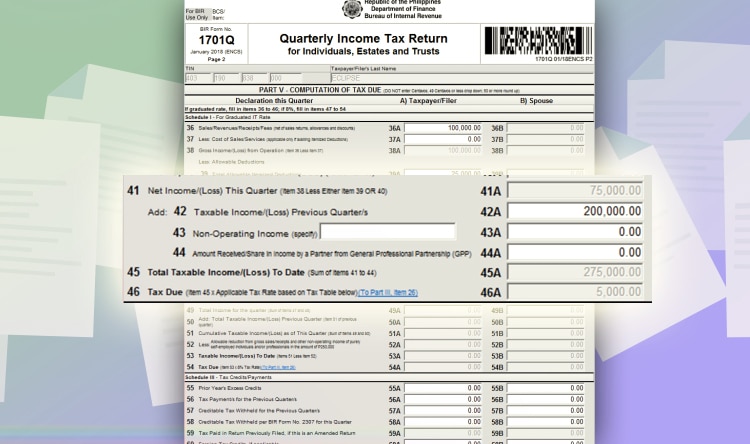
If you’re paying for the 2nd or 3rd quarter, you have to input your net income from the past quarters.
Line item 41: Input your taxable income/loss from the previous quarters. So if you earned 200,000 PHP in the last quarters, you have to fill up this line item with 200,000 PHP. And then, your tax due for the quarter will automatically be computed.
In this case, it’s 5,000 PHP tax due.
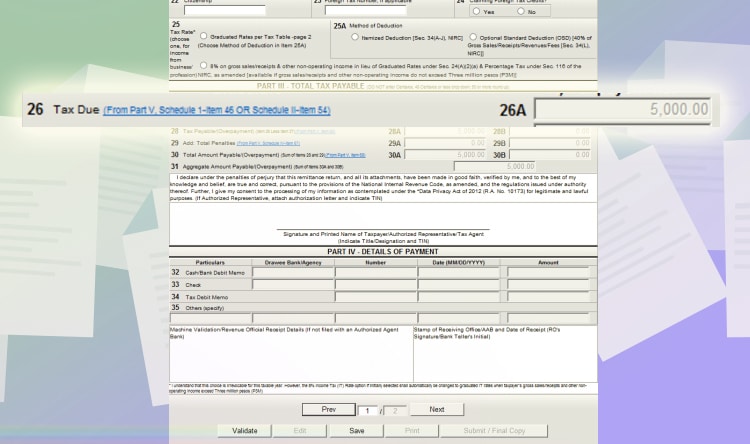
Lastly, go to the first page. It will reflect your tax due. Click validate to make sure all fields required are filled out. And then, click Submit/Final Copy.

Similar to the previous forms, you will also receive an email confirmation for your tax filing.
Quarterly Income Tax – Optional Standard Deduction
You can also choose Optional Standard Deduction if you don’t have time to track your expenses. Or your expenses are not significant enough to decrease your tax due.
For example, you have a gross sales of 100,000 PHP. Input it at line item 36. The program will automatically compute the allowable deductions for you. It represents 40% of your gross sales.
In this case, 40,000 PHP was deducted from your 100,000 PHP gross sales. And it will be automatically filled up in line item 40A.
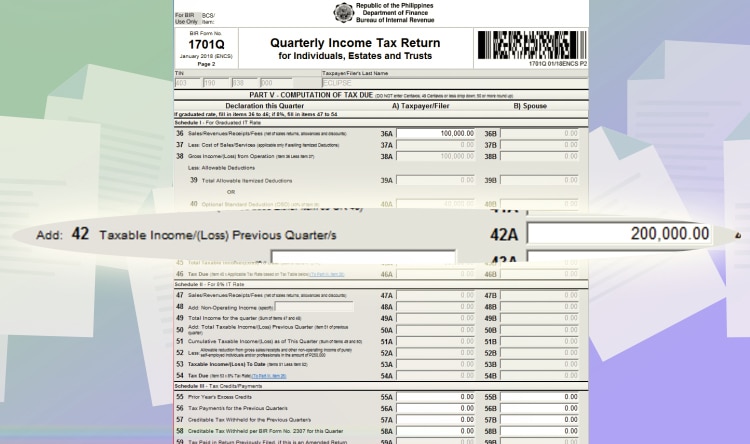
If you’re paying for the 2nd or 3rd quarter, you also have to include your past taxable income for the last quarters. Input this on Line item 42.
In this example, assuming you have 200,000 PHP taxable income from the last quarter, it will automatically compute the tax due. In this case, it’s 2,000 PHP.
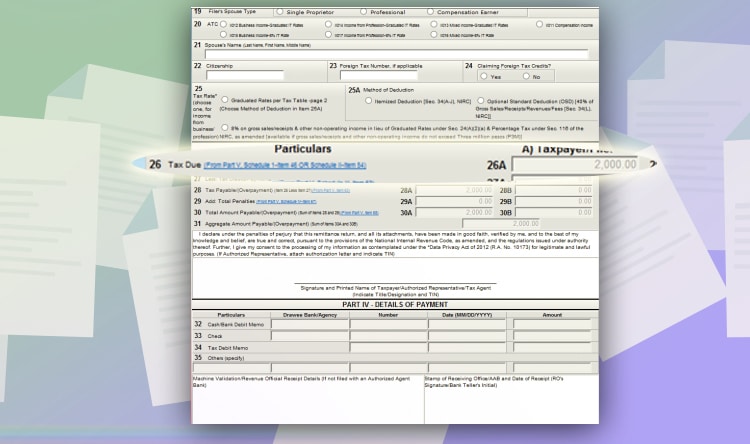
Go back to the 1st page. And it will reflect the tax due. Click validate to check if all fields are filled out. And then, click, “submit / final copy.”

You will also receive an email confirmation of your tax filing. It will serve as your proof for filing the taxes.
Quarterly Income Tax – 8% in Lieu of Percentage Taxes
Choosing the 8% tax rate is relatively easier and cost-effective to file compared to the graduate taxes. It’s especially true for remote workers and freelancers. And here’s what you need to input for the quarterly percentage taxes.
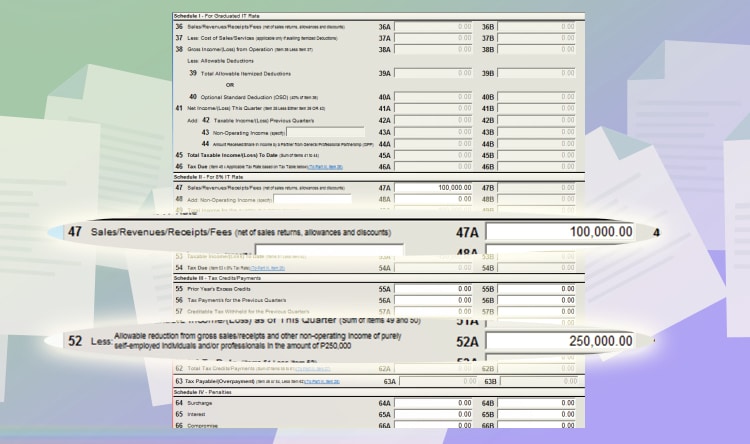
For the 8% tax rate, you will input information on the boxes in schedule 2. For example, you have a gross sales of 100,000 PHP. Input it on line item 47.
And then, don’t forget to input 250,000 on line item 52. It represents the 250,000 tax-exempt portion of every Filipino’s income. And yes, that includes you.
You don’t have to input this on the graduated income tax because the formula they use already includes the exemption already.
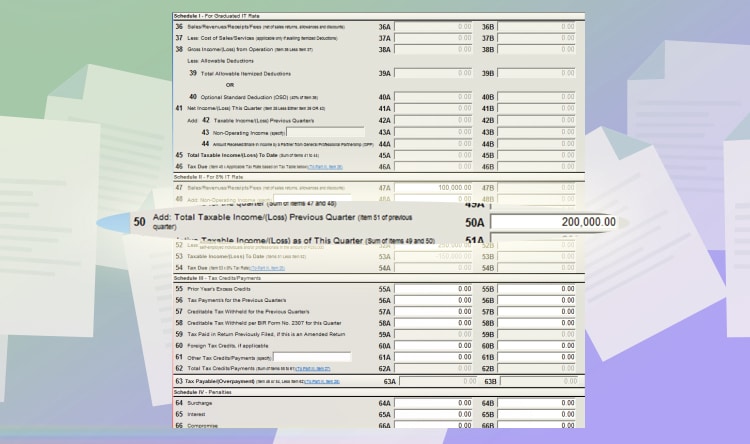
If you’re paying for the 2nd or 3rd quarter, you need to input your total taxable income for the last quarters. Fill up line item 50 for this.
For example, our past taxable income is 200,000 PHP. The program will automatically calculate the total due. In this case, it’s 4,000 PHP.
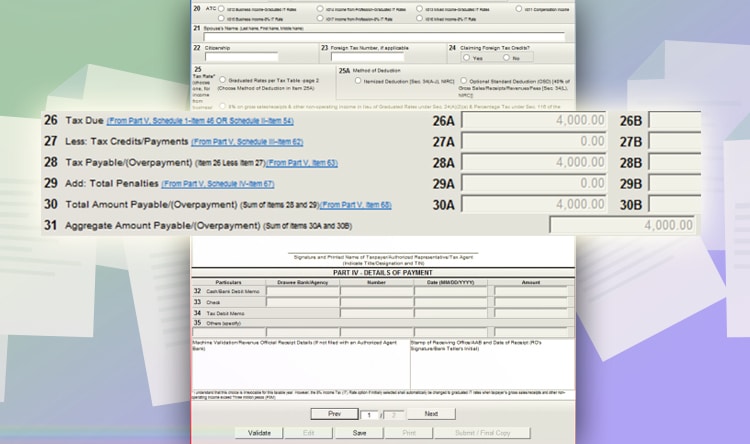
Go back to page one. You will see the tax due. Click validate to check if all fields are filled out. And then, click “submit/final copy.”

After filing, you will receive an email confirmation for the taxes filed. It will serve as proof of your tax filing.
Annual Income Tax
Now for the last part. The Annual Income tax is the tax you pay for your income for the whole year. It’s best that you get an accountant because it might be too complicated for you to fill in the required information.
But if you only have simple transactions, you can still file on your own. And here’s how to do it.
First, choose “BIR Form 1708v2018 – Annual Income Tax Return.”
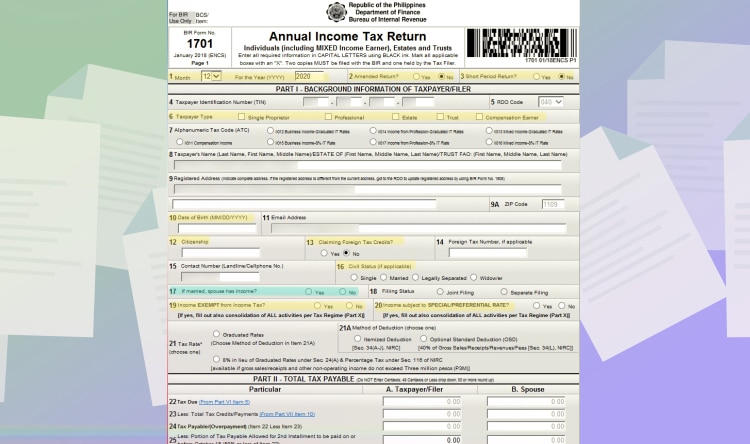
And then, fill up the following:
- Line Item 1: Pick 12 for the month and input the year
- Line Item 2: Choose No.
- Line Item 3: Choose No.
- Line Item 6: Choose Professional.
- Line Item 10: Input your date of birth.
- Line Item 12: Input your citizenship.
- Line Item 13: Choose No.
- Line Item 16: Choose your Marital Status. For the purpose of this article, we will choose Single or Married with Separate Filing for Line Item 18.
- Line Item 19: Choose No.
- Line Item 20: Choose No.
- Line Item 4, 5, 8, 9, 9A, 11: These line items will be automatically filled by your information in the main menu.
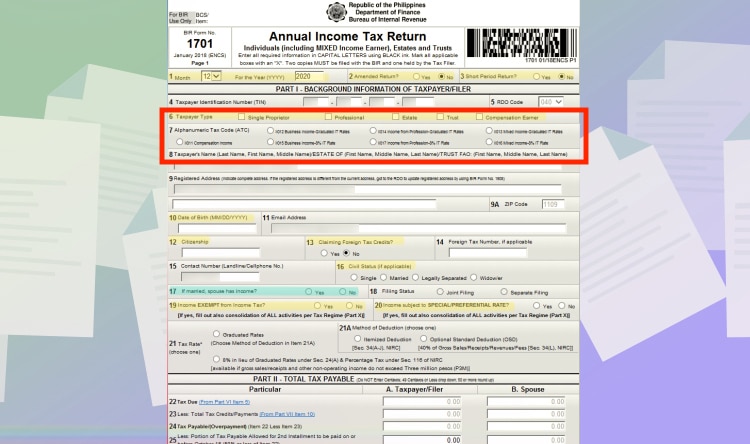
For Line Item 7, you can either choose “Income from Profession – Graduated IT Rate” or “Income from Profession – 8% IT Rate.”
For Line Item 21, it’s automatically chosen depending on Line Item 7.
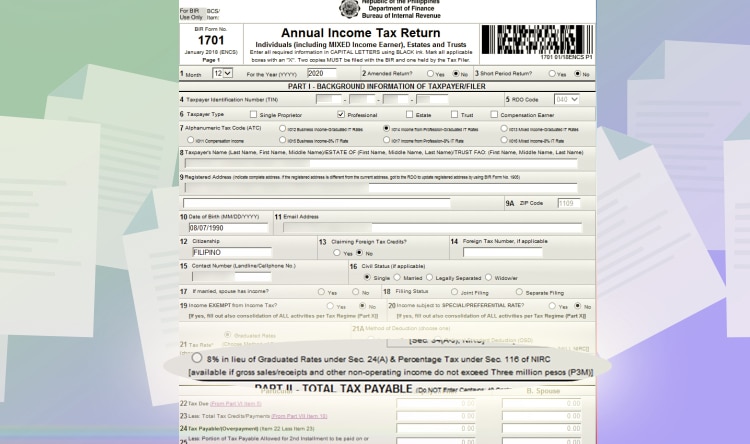
8% if you chose “Income from Profession – 8% IT Rate.”
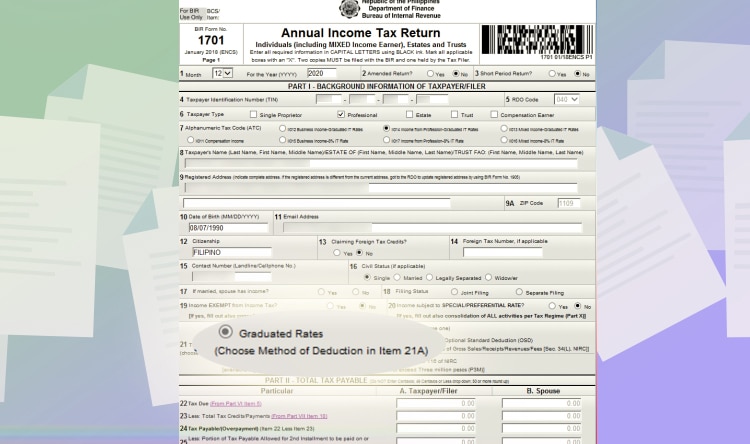
Graduated rates if you chose “Income from Profession – Graduated IT Rate.”
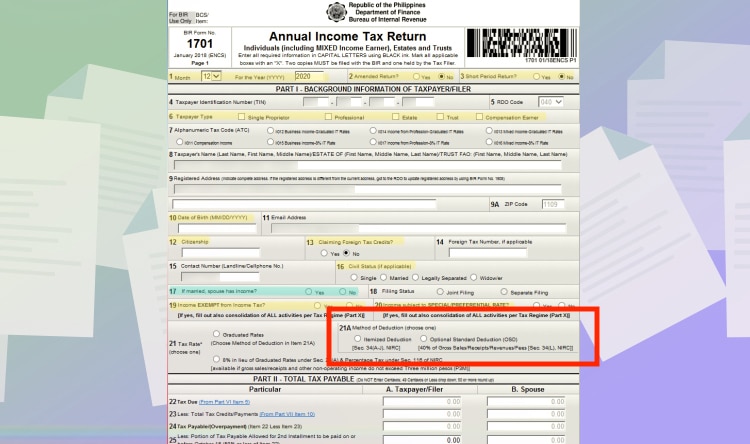
For graduated tax, you just have to choose either “Itemized Deduction” or “Optional Standard Deduction.”
Make sure that you choose the tax scheme similar to your quarterly tax returns. For example, if you’re paying using “Quarterly Graduated Income tax – Itemized Deduction”. You can’t pick Income from Profession – 8% IT Rate or change to Optional Standard Deduction.
So choose wisely from the start. And here’s how you can file depending on what you chose.
Itemized Deductions
If you chose “itemized deductions” for line item 21A, here are the steps.
Click next at the bottom page.
For your tax scheme, you need to fill up Schedule Section 3A. Here’s what you will need.
- Line Item 8: Your total sales for the whole year.
- Line Item 11: Your total expenses for the year.
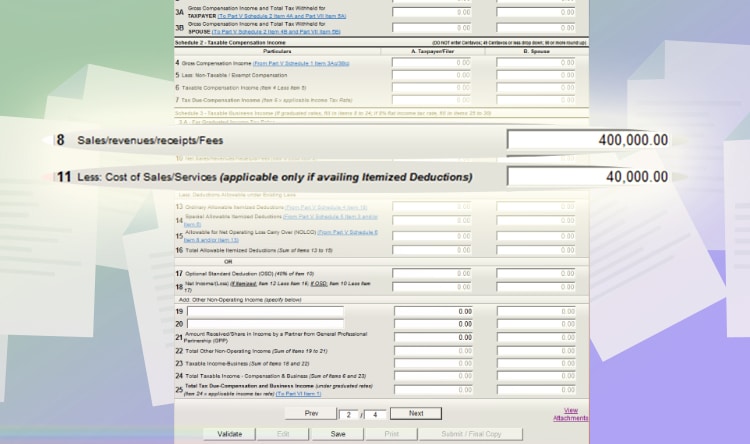
Let’s say your total sales for the year is 400,000 PHP. And your total expenses (utilities, transportation, and etc.) are 40,000 PHP. Here’s how it will look like.
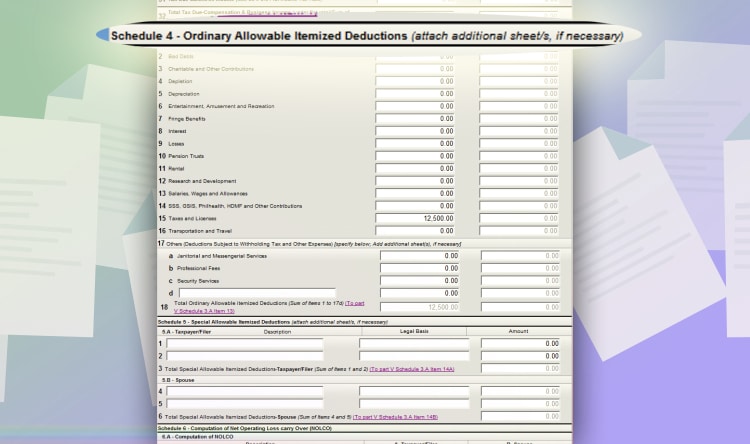
Next, go to page 3. And then, look for Schedule 4 – Ordinary Itemized Deductions. For simplicity, we will assume that you only have line item 15 “Taxes and Licenses” for your practice.
With this, just input the percentage tax and registration fee you paid for the year. For 400k income, most likely that’s 12,000 PHP (3% of 400,000 PHP) plus 500 PHP registration fee.
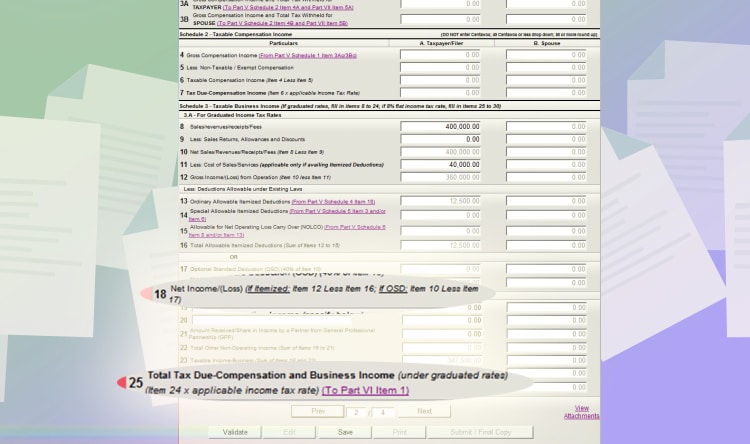
If you go back to page 2, the 12,500 PHP you inputted is accounted for. Resulting in a total Net income/loss of 347,500 PHP (line item 18), which was automatically computed by the program. Take note of this figure because you will need it on the last section of the form.
And then, line item 25 will show you your tax due for the year. But you’re not yet done filing.
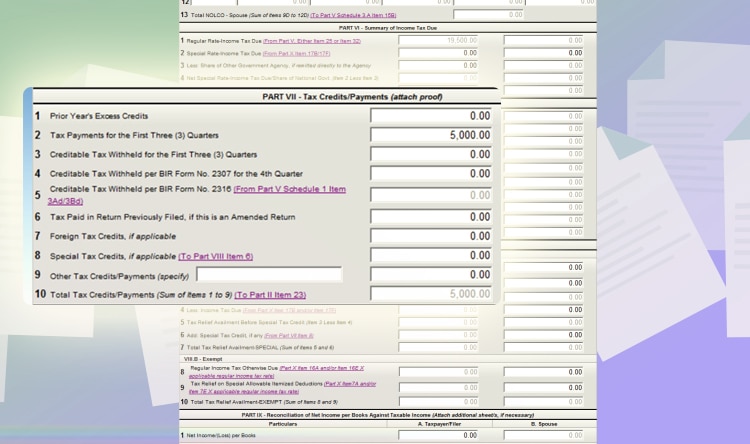
Go to page 4, and then look for PART VII Tax Credits/Payments.
If you paid your quarterly income taxes, you should include them to lessen your tax liability for the year. Let’s say 5,000 PHP like the one in our Quarterly Percentage Tax example in the previous sections. Input it on line item 2.
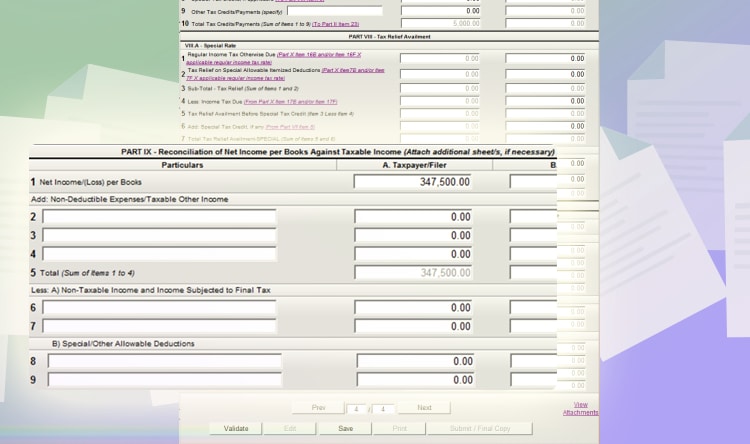
The last part is “PART IX Reconciliation of Net Income per Books Against Taxable Income.” Because of changing principles of accounting and the definition of income and expenses by the government, there might be a difference between taxable income based on your books. The purpose of this section is to reconcile the difference.
For simplicity purposes, we will assume that you only have simple transactions for your freelancing practice. Therefore, there will be no changes between Net Income per books with the net taxable income.
With this, just input the amount on “line item 18:Net Income/Loss” on page 2 to line item 1. For this example, you have the same 347,500 PHP.
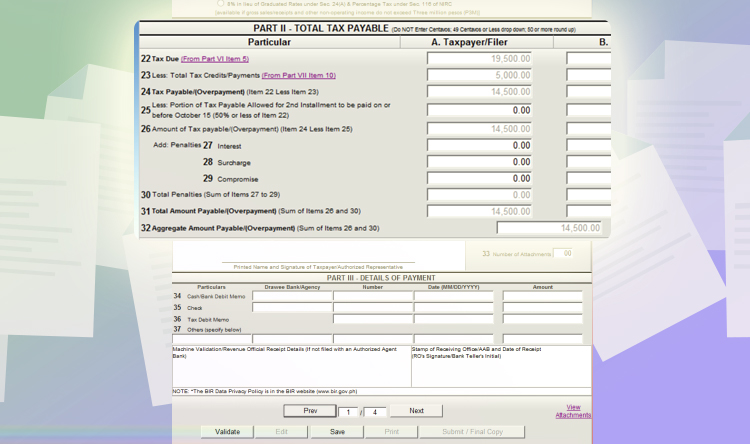
Lastly, go to page 1. You will see a summary of the line items for your tax liability. Click validate to check if there are other fields not filled up. And then, click “Submit/Final Copy.”

Similar to the other taxes, an email confirmation of your tax filing will be sent. It will serve as your proof when passing your forms to BIR and other agencies, just in case you need to.
Optional Standard Deduction
The optional standard deduction is a less complicated option if you don’t have the time for tracking your expenses. It’s also beneficial if you don’t have too many expenses as well. Regardless of your actual expenses, it deducts a fixed rate of 40% as your expenses. And here’s what you need to file.
On line item 21A, click optional standard deduction.
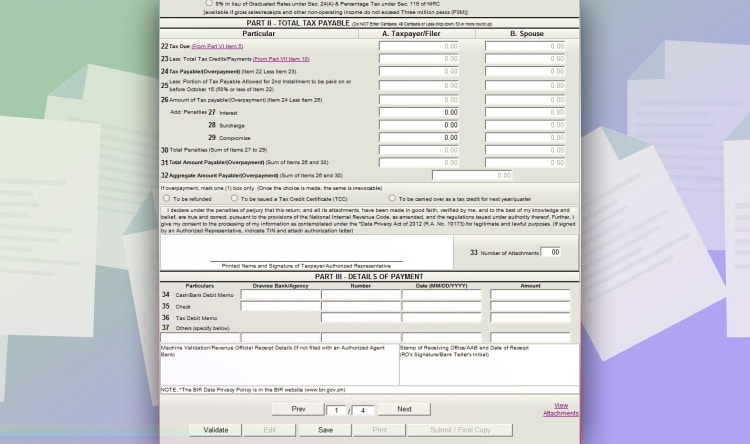
And then, click next to go to page 2.
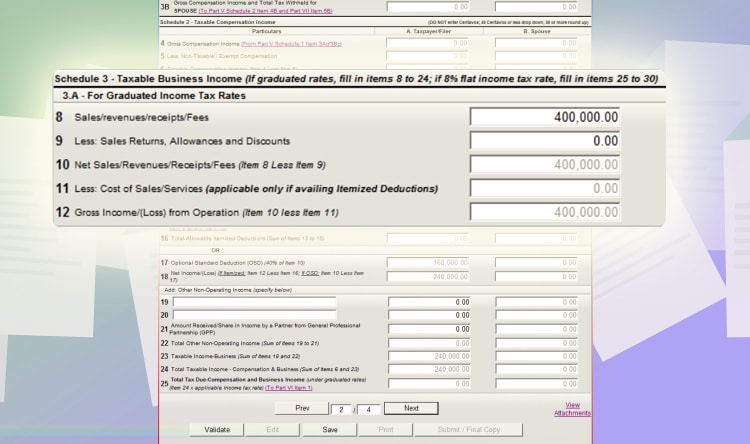
Go to schedule 3. And just your total sales on line item 8. In this example, let’s also input 400,000 PHP. A total of 160,000 PHP (or 40% of 400,000 PHP) will be your expenses.
The program will automatically compute your tax due, which is zero because income below 250,000 PHP is tax-exempt. In this case, you only have 240,000 PHP net income.
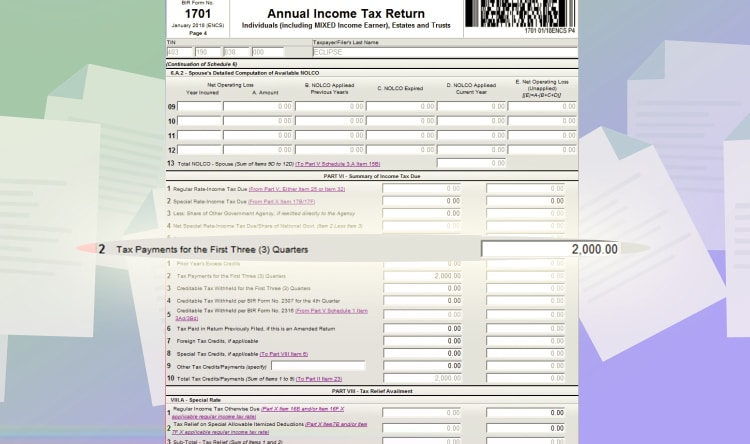
And then, go to page 4 if you paid any quarterly income taxes. In this example, assuming you paid 2,000 PHP quarterly income tax. Input it on line item 2 under Part VII – Tax credits/Payments.
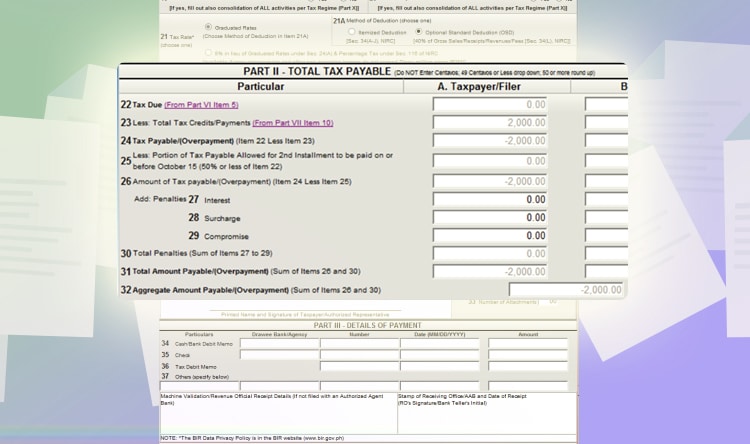
Afterwards, go to the first page. You will see a summary of your tax due. In this case, you will have a tax credit of 2,000 PHP because of overpayment. Click validate to check if all fields are filled out. And then, click “submit/final copy.”

An email confirmation of your tax filing will be sent. It will serve as your proof when passing your forms to BIR and other agencies, just in case you need to.
8% Tax in Lieu of Percentage Taxes
To make it even simpler, the government proposed the 8% tax rate in lieu of percentage taxes. It allows taxpayers to pay only 8% without the need to file percentage taxes.
It might be more cost-effective and convenient for remote workers because they don’t have a lot of expenses. Most of the time, it’s even more advantageous than the Optional Standard Deduction. And here’s what you need to input.
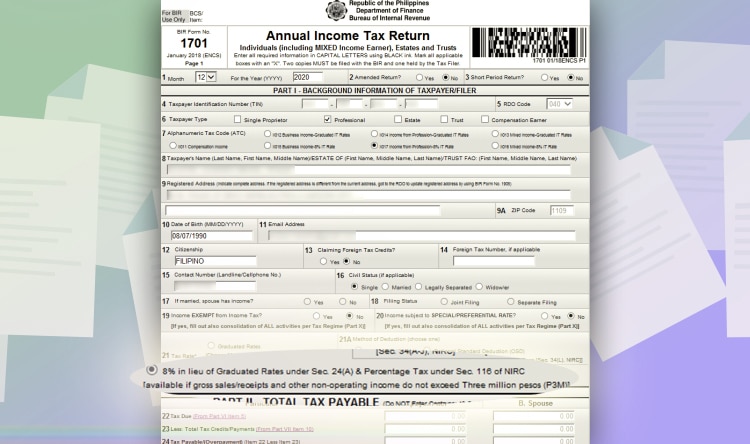
Choose “Income from Profession – 8% IT rate” on line item 7. It will automatically pick the 8% tax rate on line item 21.
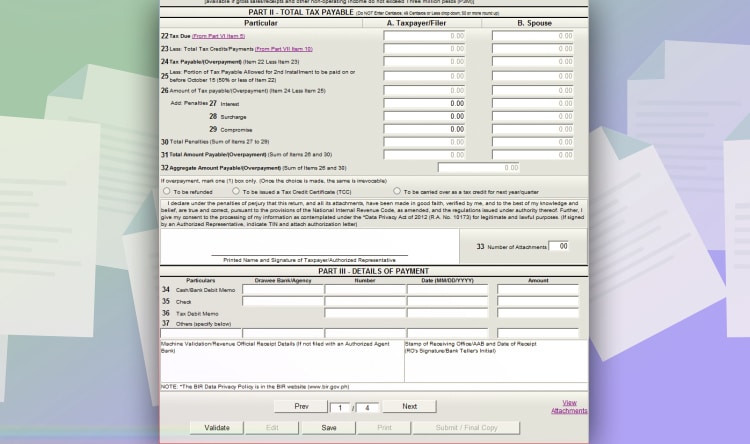
And then, click next up to page 3.
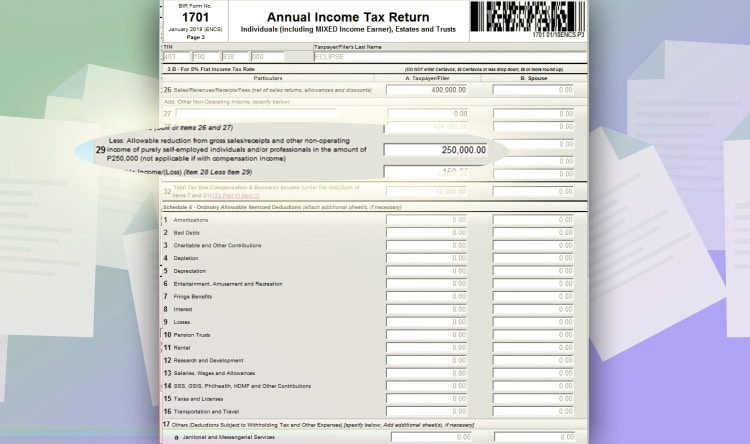
Input your total gross sales on line item 26. And then, don’t forget to put 250,000 PHP on line item 29 for the tax-exempt. It will automatically compute your tax due for the year.
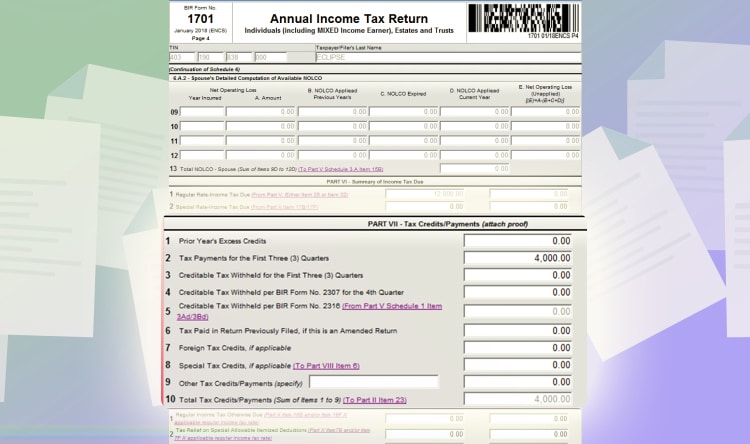
Next, go to page 4 and look for Part VII – Tax Credits/Payments. And on line item 2, any tax payments you made for the past quarters. In this example, let’s assume you paid 4,000 PHP.
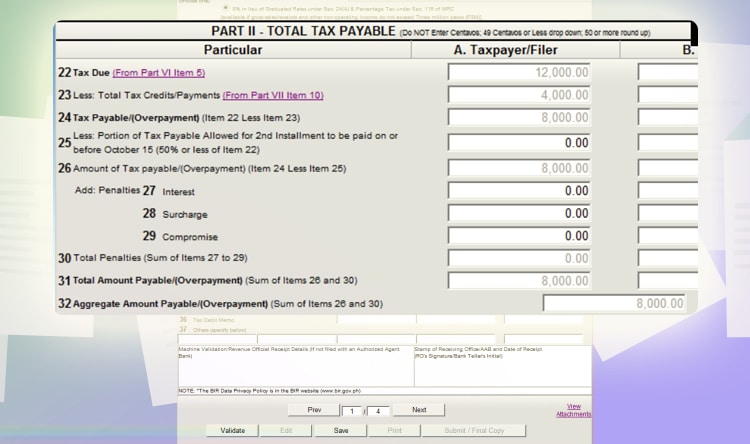
Lastly, go to page one. And you will see a summary of the remaining tax due for the year. Click validate to check fields that aren’t filled out. And then, click “submit/final copy.”

You will get an email confirmation of your tax filing. It will serve as proof of filing.
Paying for Your Taxes
You can opt to pay your taxes with the specific Authorized Agent Banks per RDO Branch. You can find the list on this link. You just need to bring three copies of the form you’re paying for. And pay at the nearest Authorized Agent Bank.
But is there a way to pay online? There actually is! The same you pay your Mandatory benefits, you can also pay your taxes using Paymaya or Gcash. This is how you can do it.
Paying through Paymaya
For Paymaya, here are the steps.
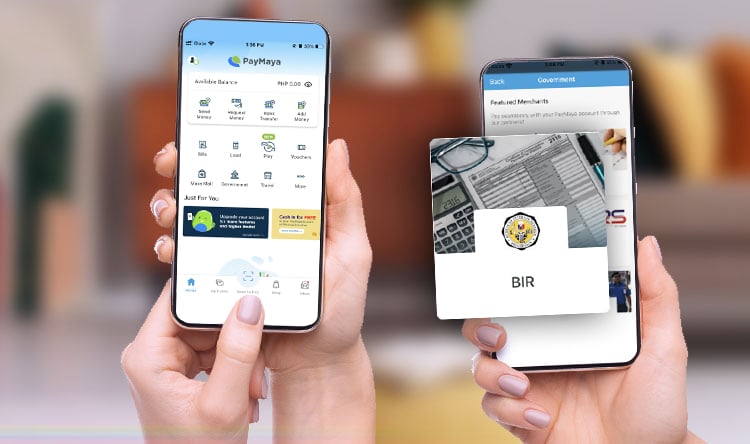
Open the Paymaya App and click “Government.” And then, choose BIR.
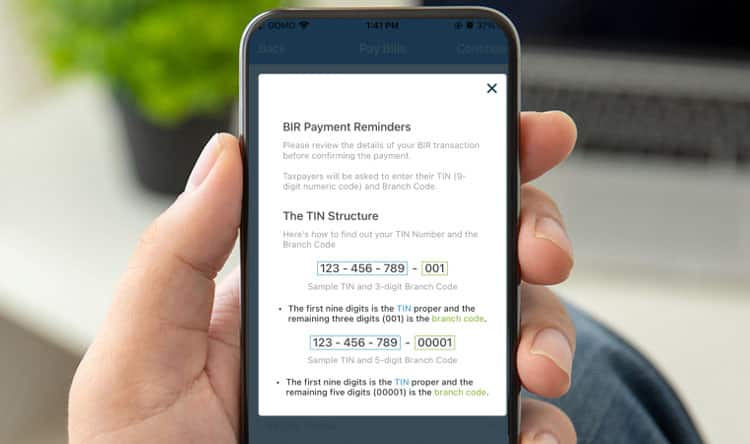
A pop-up will show to guide you on the fields to be filled up.
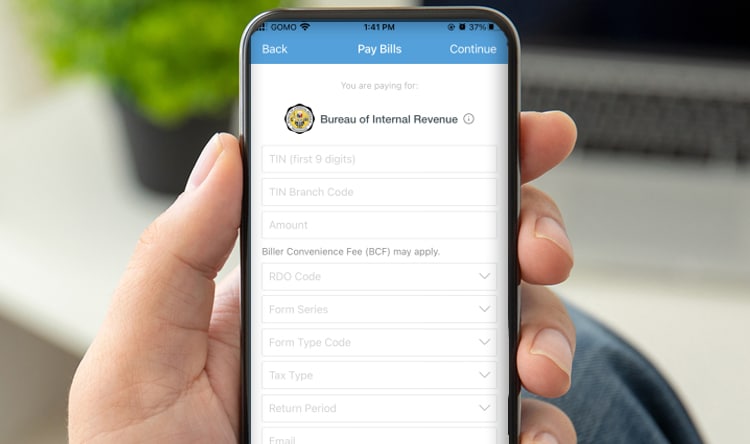
And then, fill up the information needed. It’s best to check your digital copy to avoid mistakes. Click continue afterwards. A small convenience fee might be charged for the transaction.
And that’s it! You’ve paid your taxes through Paymaya. Make sure to get a screenshot as well of the payment for documentation purposes.
Paying through Gcash
You can also pay your tax due through Gcash.
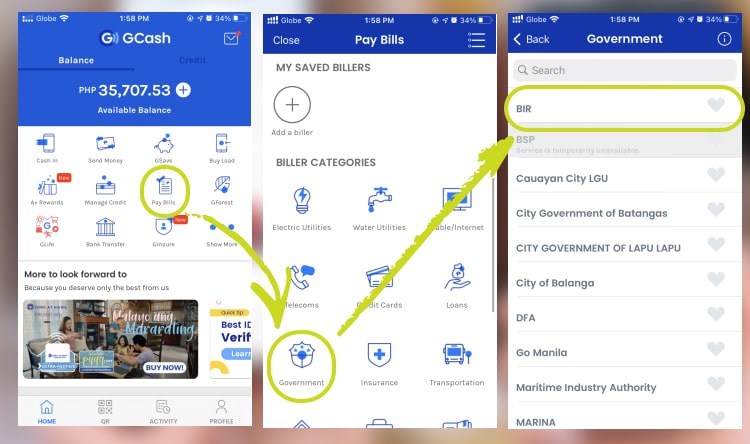
Just open your Gcash account and click “Pay Bills.” And then, click “Government” and choose BIR.
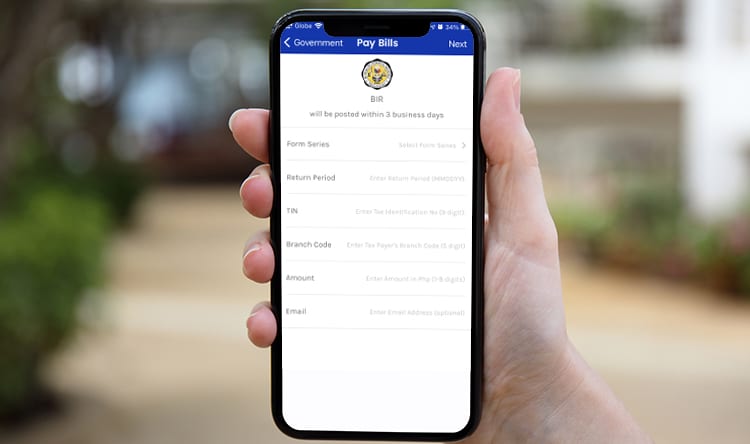
From there, just fill up the information needed. Just like in Paymaya’s guide, the branch code will be the last three digits of your TIN.
So for example, your TIN is 123 – 456 – 789 – 000. The branch code is 00 000. It represents the last three numbers with an additional 2 zeros at the beginning.

Conclusion
After that, you’re done! You have successfully filed and paid your tax returns! If you’re looking for remote work, you can check out the following high-paying jobs that you can take advantage of. Cheers!